Conservative Management for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Introduction
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common condition affecting the hand and wrist, characterized by pain, numbness, and tingling due to compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel. While severe cases may require surgical intervention, conservative management options are often the first line of treatment for individuals experiencing mild to moderate symptoms. This article will explore the various conservative management strategies for carpal tunnel syndrome and their potential benefits.
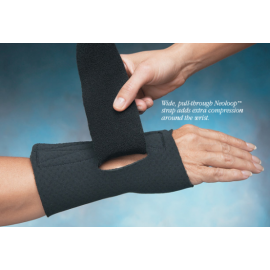
Wrist Splinting
One of the most common conservative treatments for CTS is the use of a wrist splint. Wrist splints are designed to maintain the wrist in a neutral position, minimizing pressure on the median nerve. Splints are often worn during sleep, as individuals may unknowingly bend their wrists during the night, exacerbating symptoms. In some cases, wearing a splint during activities that aggravate symptoms may also provide relief.
Activity Modification
Identifying and modifying activities that contribute to CTS symptoms is an essential aspect of conservative management. This may involve adjusting the ergonomics of a workspace, taking frequent breaks, or modifying hand and wrist movements to reduce strain on the median nerve. Occupational therapists can provide valuable guidance in identifying and addressing the factors contributing to CTS.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. However, these medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as long-term use may have adverse effects.
Hand and Wrist Exercises
Specific exercises and stretches targeting the hand and wrist may help improve symptoms of CTS by promoting blood flow, reducing inflammation, and improving nerve gliding. A physical or occupational therapist can recommend appropriate exercises tailored to an individual's needs and monitor progress.
Cold and Heat Therapy
Applying cold packs to the affected wrist may help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain. Heat therapy, such as warm compresses or soaking the hand in warm water, can help relax the muscles and improve blood flow in the area. Alternating between cold and heat therapy may be beneficial for some individuals.
Corticosteroid Injections
In cases where conservative measures do not provide sufficient relief, corticosteroid injections may be considered. These injections, administered by a healthcare professional, can help reduce inflammation around the median nerve and provide temporary relief from symptoms. However, corticosteroid injections may not be suitable for all individuals and are generally not considered a long-term solution.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Some individuals may find relief from CTS symptoms through complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or massage. While the effectiveness of these treatments may vary, they may provide additional symptom relief when used alongside other conservative management strategies.
Conclusion
Conservative management for carpal tunnel syndrome involves a variety of non-surgical treatment options aimed at reducing pressure on the median nerve and alleviating symptoms. Wrist splinting, activity modification, NSAIDs, hand and wrist exercises, cold and heat therapy, corticosteroid injections, and complementary therapies may all play a role in the successful management of CTS. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to the specific needs and severity of symptoms.


-270x270.png)


Leave your comment
Note: HTML is not translated!